What Is the Network Topology and Why Does It Matters?
Have you ever wondered how computers connect and share information in a smooth and organized way? That’s where network topology comes in. It defines how devices are arranged and linked in a computer network. Just like roads connect cities, cables and wireless signals connect computers. From small office setups to global systems like the internet topology, understanding these network types helps you grasp the core of networking basics. To fully appreciate how computers work in these networks, take a look at what makes a computer truly powerful — it all starts with the core features inside the machine.
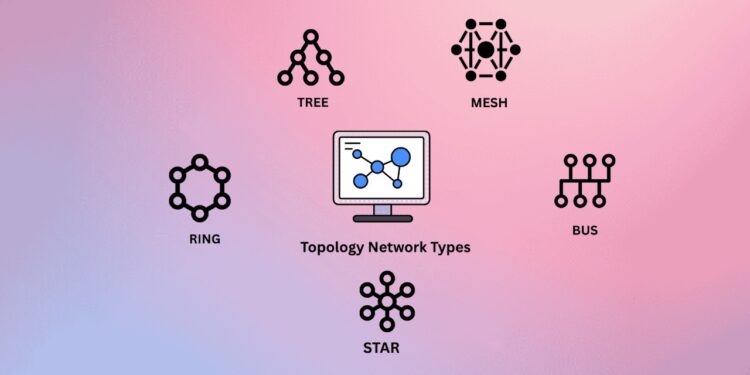
Types of Topology in Computer Networking
Topology refers to the structure or layout of how different devices, also called nodes, are connected in a network. Each setup has its own way of handling data flow, performance, and maintenance. Let’s explore the most common types:
1. Bus Topology
All devices are connected to a single central cable. This setup is simple and cost-effective, especially for small networks. However, if the main cable fails, the whole network goes down. The bus topology is one of the simplest and oldest methods. All computers or nodes connect to a single central cable, known as the backbone. Data travels in both directions along this main cable, and each device listens for its data. Although it’s cost-effective and easy to set up, a single fault in the cable can break down the entire communication line. It’s mostly used in smaller LAN structures or older network designs.
2. Star Topology
This is one of the most widely used topologies in modern computer networks. It’s easy to manage and isolate issues, but if the central hub fails, none of the devices can communicate.
Another widely used design is the star topology, where all devices connect to a central hub or switch. This setup is common in modern home and office networks. One of the key benefits is that if one cable or device fails, the rest of the network keeps working. It’s easy to manage and expand, which is why it’s preferred for growing businesses and schools.
3. Ring Topology
Here, each device is connected in a circular loop. Data travels in one direction, and each device passes the data to the next. While it ensures smooth data transfer, a single failure can affect the whole loop.
The ring topology connects each device to two others, forming a circular path. Data moves in one direction, passing through each device until it reaches its destination. Although this provides orderly data flow, a break in the circle can stop communication altogether. Some older educational and business networks used ring setups, but they’ve become less common today.
4. Mesh Topology
In a mesh setup, every device is connected to every other device. This improves reliability and data speed, especially in larger networks. It’s often used in internet topology where speed and fault tolerance are crucial.
Next is the mesh topology, which offers a highly reliable connection between all devices. Every node is connected to every other node in the network. This layout provides multiple data paths, so if one connection fails, another path can be used. Mesh topologies are often seen in internet topology frameworks, military systems, or large communication networks where high availability is crucial. The downside is that this topology requires more cabling and configuration, making it expensive and harder to maintain.
5. Hybrid Topology
This topology is the combination of two or more different topologies, like star and bus or mesh and ring. It gives flexibility and can be customized based on the network types and specific needs. Lastly, the hybrid topology combines two or more topologies to create a flexible and customized network. For example, a combination of star and bus topology is often used in large organizations and universities. This setup allows for better control, performance, and scalability but may also increase design complexity and cost.
Final Thoughts on Understanding Network Topology
To sum it up, network topology is the foundation of any computer network. Choosing the right layout improves speed, reduces errors, and makes data sharing easier. Whether it’s a home network or part of the internet topology, knowing different network types gives you better control over how information flows. If you’re learning networking basics, topology is one of the first and most important things to understand. It’s the map that guides your entire digital world.